The broadening wedge pattern is a chart setup defined by diverging trendlines that form a megaphone shape, signaling increasing market volatility. Traders watch these patterns closely because they often precede significant price movements. Here’s what you need to know:
- Key Features: Diverging trendlines, at least five price touchpoints, and rising volume.
- Types:
- Ascending Broadening Wedge: Typically bearish, with upward-sloping trendlines and frequent downward breakouts.
- Descending Broadening Wedge: Generally bullish, with downward-sloping trendlines and upward breakouts.
- Trading Tips:
- Confirm breakouts with a candle close beyond the trendline and a volume surge.
- Use stop-loss orders near the breakout zone or recent swing points.
- Target profits by measuring the pattern’s height and projecting it from the breakout point.
- Market Behavior:
- In stocks, these patterns often align with bull markets.
- In forex, breakout directions are closer to 50/50.
- In crypto, they highlight extreme volatility.
Broadening wedges require patience and careful risk management due to their volatile nature. Recognizing the setup, confirming breakouts, and setting clear entry and exit points can help you trade them effectively.
📈Broadening Wedge (Chart Patterns & Price Action Explained)
How to Identify a Broadening Wedge Pattern
Understanding the dynamics of a broadening wedge pattern is one thing, but spotting it on a chart requires attention to detail. Let’s break down the key visual cues and common mistakes to help sharpen your analysis.
Visual Features of Broadening Wedges
A broadening wedge stands out with its diverging trendlines, forming a shape that looks like a megaphone. This expanding structure sets it apart from other patterns, like standard wedges or triangles, where the lines converge.
To confirm the pattern, look for at least five distinct touchpoints – usually three on one trendline and two on the other. Note that price crossings alone don’t count.
The peaks and troughs should progressively expand, creating what looks like "saw teeth." If the price swings start to shrink instead of growing, you’re likely dealing with a different formation.
Another key indicator is volume. Unlike patterns with declining volume, broadening wedges usually show rising volume, reflecting the growing tug-of-war between buyers and sellers.
By focusing on these clear markers, you can improve your ability to spot this pattern. However, there are also some common traps to avoid.
Common Charting Errors to Avoid
One frequent mistake is forcing trendlines to fit. Use only valid minor highs and lows to draw the lines. Adjusting them to "make the pattern work" often leads to incorrect analysis.
Another error is leaving too much space between the trendlines and the price. A true broadening wedge has prices that regularly crisscross its boundaries.
It’s also easy to confuse broadening wedges with standard triangles or wedges. The main difference? Broadening wedges have diverging trendlines, signaling growing volatility, while triangles and standard wedges feature converging lines.
Finally, remember that broadening wedges occur in high-volatility markets. Calm, steady conditions won’t produce the large, expansive swings that define this pattern.
Ascending vs. Descending Broadening Wedges
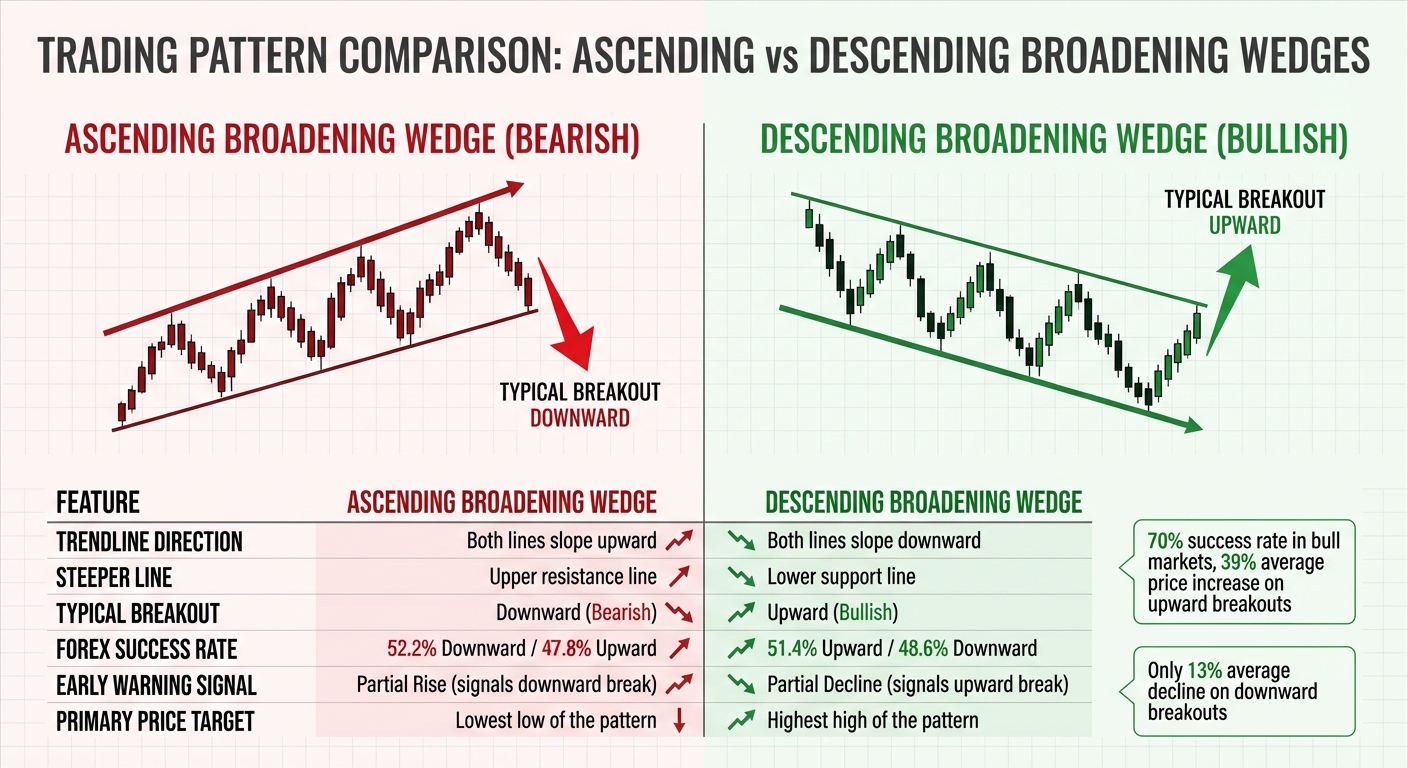
Ascending vs Descending Broadening Wedge Pattern Comparison Chart
Both ascending and descending broadening wedges share the same expanding, megaphone-like structure. However, the direction of their trendlines creates distinct patterns and biases, which can help traders align their strategies with market movements.
An ascending broadening wedge features two rising trendlines, with the upper resistance line climbing at a steeper angle than the lower support line. This setup often signals a bearish bias, meaning it tends to break downward. In forex markets, these patterns lead to downward corrections about 52%-55% of the time.
On the flip side, a descending broadening wedge has two falling trendlines, where the lower support line drops more sharply than the upper resistance line. This pattern generally favors upward breakouts, with success rates around 70% in bull markets and approximately 51% in forex trading.
"Ascending broadening wedges have a bearish bias with breakouts mostly occurring downward." – Sean Mackey, Founder & CEO, LuxAlgo
Recognizing Early Signals
Spotting early warning signs in these patterns can sharpen your trading decisions:
- In ascending wedges, a failure to reach the upper resistance line during a bounce off the lower trendline often indicates a downward breakout. This prediction holds true in over 79% of cases.
- In descending wedges, a failure to touch the lower support line during a drop from the upper resistance line often signals an upward breakout.
Identifying these cues can help traders fine-tune their stop-loss placements and improve risk management.
Comparison Table: Characteristics and Outcomes
| Feature | Ascending Broadening Wedge | Descending Broadening Wedge |
|---|---|---|
| Trendline Direction | Both lines slope upward | Both lines slope downward |
| Steeper Line | Upper resistance line | Lower support line |
| Typical Breakout | Downward (Bearish) | Upward (Bullish) |
| Forex Success Rate | 52.2% Downward / 47.8% Upward | 51.4% Upward / 48.6% Downward |
| Early Warning Signal | Partial Rise (signals downward break) | Partial Decline (signals upward break) |
| Primary Price Target | Lowest low of the pattern | Highest high of the pattern |
Trading Tips for Wedges
For ascending wedges, entering a short position when the price breaks below the midline of the pattern can be a smart move. This approach has a 53% success rate, slightly outperforming trades that wait for the full support line to be breached. Meanwhile, with descending wedges, upward breakouts tend to result in an average price increase of 39%, while downward breakouts typically lead to only a modest 13% decline. This reinforces the bullish tendency of descending broadening wedges.
sbb-itb-24dd98f
How to Trade the Broadening Wedge Pattern
Once you’ve identified the broadening wedge pattern, the next step is executing trades with precision. This requires a steady hand – waiting for confirmed breakouts, placing tight stop losses, and keeping your position sizes manageable in the face of volatility. Below, we’ll walk through key strategies for entering and exiting trades, as well as managing risk effectively.
Confirming Breakouts and Entry Timing
Timing is everything when trading a broadening wedge. Only enter a trade after a candle closes clearly beyond the pattern’s boundary. To avoid false signals, wait for the next candle to also close outside the pattern. A surge in trading volume is another critical indicator that confirms the breakout.
In ascending wedges, breaking below the midline often provides a more reliable entry point than waiting for the lower support line to give way. Statistically, a midline break has a 53% success rate, while a break of the support line rebounds 50.7% of the time. For descending wedges, an upward breakout is correctly predicted 79% of the time when the price fails to reach the lower trendline during a drop from resistance. Since broadening wedges have throwback rates exceeding 60%, it can be wise to wait for the price to retest the broken trendline before committing to a trade.
Once the breakout is confirmed, it’s time to set your stop loss and define your profit targets.
Setting Stop Loss and Take Profit Levels
Position your stop loss just beyond the breakout zone or on the opposite side of the trendline. For short positions in an ascending wedge, place the stop above the last swing high. For long positions in a descending wedge, set the stop below the most recent swing low. Adding a buffer using the 14-period ATR (Average True Range) can help avoid being stopped out prematurely.
To determine your profit target, measure the maximum height of the pattern and project that distance from the breakout point. If an ascending wedge breaks downward, aim for the pattern’s lowest point. Conversely, if a descending wedge breaks upward, target the highest high. Always ensure your risk-reward ratio is at least 2:1, meaning your potential profit should be at least double the distance to your stop loss. If the trade doesn’t meet this ratio, it’s better to skip it. As prices move in your favor, consider using a trailing stop or moving your stop to the breakeven point to protect your gains from sudden reversals.
Managing Risk in Volatile Conditions
Broadening wedges often signal heightened volatility, so reducing your position size is a smart move. As Kestutis Balciunas explains:
"The broadening price action indicates volatile conditions ahead. Size positions smaller than normal."
Stick to your predetermined exit points to avoid emotional decisions during wild price swings. Using momentum indicators like RSI or MACD can also provide additional confirmation of trend changes. For example, in an ascending wedge, if the price action clusters in the upper half of the pattern, it often signals an upcoming bearish break.
Using Broadening Wedges Across Markets and Timeframes
Spotting broadening wedges in real-time takes more than just recognizing the pattern – it also requires understanding how different markets and timeframes influence their behavior.
Market-Specific Differences
Broadening wedges don’t act the same across all markets. In stock markets, these patterns often show up during bull markets and tend to favor upward movement. For example, a descending broadening wedge in a bull market breaks upward 72% of the time, with an average price increase of 39%. On the flip side, downward breakouts are less reliable, averaging a 13% drop and failing 35% of the time.
In forex markets, the odds are much closer to even. Wedges here show nearly a 50/50 chance of breaking upward or downward. This balanced probability means forex traders need to stay adaptable and avoid assuming a specific direction just because of the wedge type.
For cryptocurrency markets, broadening wedges often highlight zones of extreme volatility, where price swings widen rapidly over short periods. Given crypto’s high volatility, these patterns are common. However, confirming moves with volume is crucial to separate meaningful price action from random fluctuations.
While market type plays a significant role, the timeframe you choose to trade can also have a major impact on how these patterns perform.
Timeframe Considerations
The timeframe you’re working with can change how reliable a broadening wedge is. On shorter timeframes, wedges form more frequently, giving day traders opportunities to trade the swings between support and resistance without waiting for a breakout.
Longer timeframes, on the other hand, tend to produce more dependable breakout signals but require more patience. Taller, wider patterns generally outperform shorter, narrower ones. For instance, when a broadening wedge forms after a long-term uptrend lasting over six months, upward breakouts are often stronger. However, wedges that appear at the tail end of multi-year trends are riskier and more prone to failure. Additionally, wedges on extended timeframes tend to keep expanding, making it harder to pinpoint the exact breakout moment.
Conclusion: Trading Broadening Wedges Successfully
Trading broadening wedges effectively comes down to spotting the pattern, executing trades with precision, and managing risks wisely. To confirm a valid setup, ensure the pattern shows at least five trendline touches – typically three on one side and two on the other. These diverging trendlines and expanding price swings reflect a battle between buyers and sellers, and jumping in too early could lead to false breakouts.
Once you’ve identified the setup, timing is everything. Wait for a candle to close outside the trendline, ideally accompanied by a volume spike, to confirm the breakout. Set stop-loss orders beyond the opposite trendline or the last swing high/low to protect against reversals. Given the larger price swings these patterns produce, you might want to trade smaller position sizes to account for the added volatility.
"Mastering broadening wedge trading strategies requires patience, discipline, and adaptability to volatile price swings." – Kestutis Balciunas, Investor
After securing a solid entry, focus on refining your risk-reward approach. Measure the pattern’s height to set realistic profit targets. In forex trading, the odds of success hover closer to 50/50, so avoid making assumptions about direction based solely on the wedge type. Tools like RSI or MACD can help fine-tune your timing and confirm momentum.
To set profit targets, use the pattern’s maximum height and project that distance from the breakout point. Historical data shows that upward breakouts hit their target 83% of the time, compared to just 32% for downward moves. Trailing stops can be a great way to lock in gains as the price moves in your favor.
FAQs
What’s the difference between an ascending and descending broadening wedge?
An ascending broadening wedge appears when the price forms higher highs and higher lows. This creates two trendlines that slope upward while diverging from each other. Such a pattern often points to growing bullish momentum, with traders closely monitoring for a potential breakout above the upper trendline.
On the flip side, a descending broadening wedge develops when the price produces lower highs and lower lows. This results in downward-sloping, diverging trendlines, indicating increasing bearish pressure. Traders commonly look for a breakdown below the lower trendline in this scenario.
The main difference between the two patterns lies in the direction of the trendlines (upward for ascending, downward for descending), the sequence of highs and lows, and the likely breakout direction – bullish for ascending wedges and bearish for descending ones.
How can I confirm a breakout in a broadening wedge pattern?
To confirm a breakout in a broadening wedge pattern, here’s what you should focus on:
- Wait for a decisive candle close beyond the trendline: A breakout is only reliable when the price closes above the upper trendline (for a bullish breakout) or below the lower trendline (for a bearish breakout). This approach filters out misleading signals from intraday price swings.
- Watch for a volume spike: A genuine breakout is often accompanied by a noticeable increase in trading volume. This indicates strong participation from buyers or sellers, adding credibility to the move.
- Use momentum indicators for confirmation: Tools like the RSI or MACD can help gauge the breakout’s strength. For instance, a rising RSI crossing above 50 or the MACD line moving above the signal line can support a bullish breakout scenario.
By combining these steps, you can validate a breakout with greater confidence and align it with your trading strategy while keeping risks under control.
Why is risk management important when trading broadening wedge patterns?
Broadening wedge patterns can be tricky to trade due to their high volatility and the frequent occurrence of false breakouts. If you’re not careful, unexpected price movements can lead to steep losses.
To help safeguard your trades, stop-loss orders are a must. They act as a safety net, limiting potential losses if the market turns against you. Additionally, it’s smart to risk only a small percentage of your trading capital on each trade. Over-leveraging might seem tempting, but it can quickly spiral into unmanageable losses. Sticking to a clear, disciplined trading plan is equally crucial. By keeping your risk under control, you’ll be better equipped to handle the unpredictable nature of broadening wedge patterns while protecting your overall account balance.



