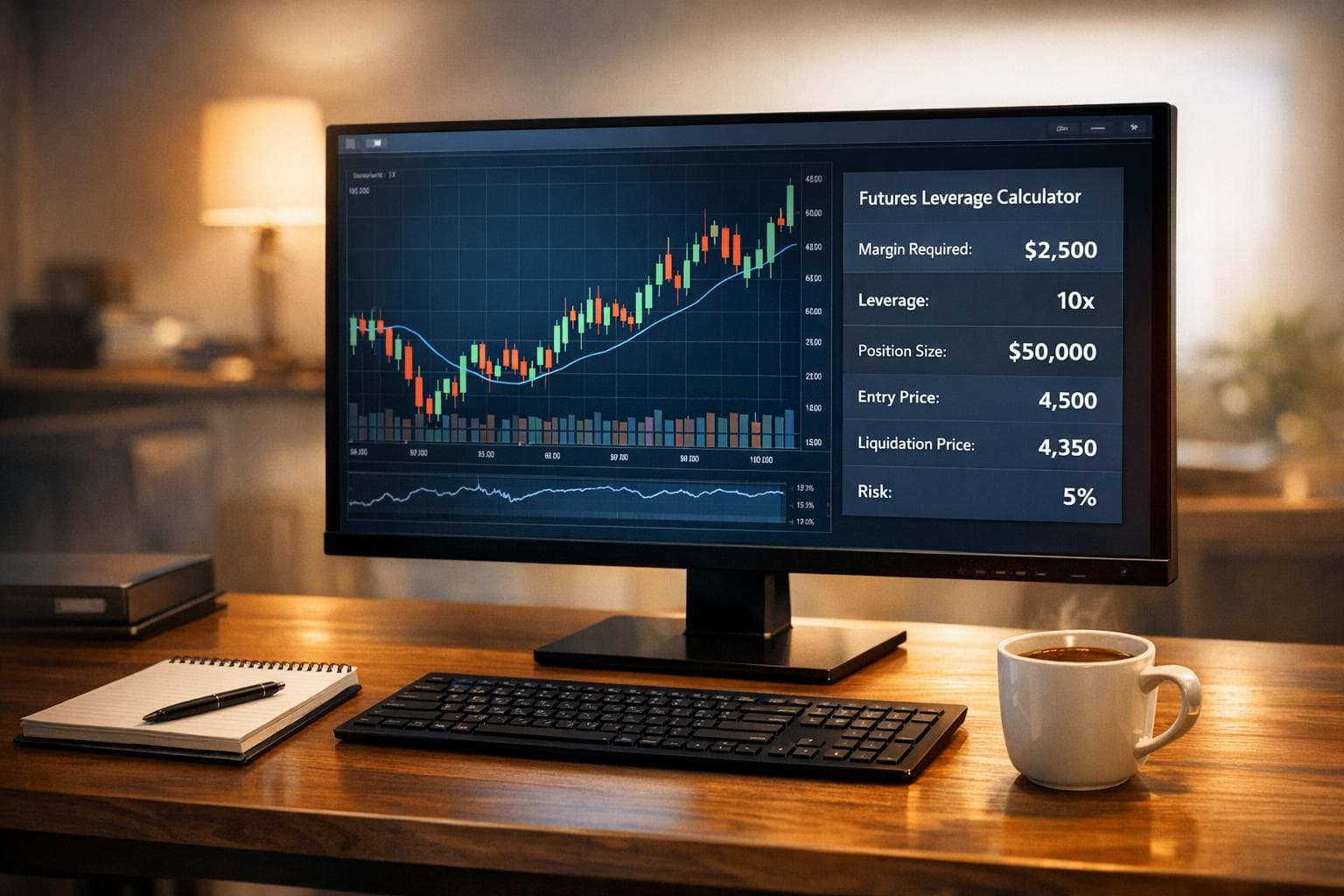
A futures leverage calculator helps traders calculate the capital needed to manage leveraged positions effectively. By using inputs like account size, leverage, position size, entry price, and stop-loss, it provides key metrics such as margin requirements, position sizing, and risk/reward ratios. This tool ensures traders can assess risk, avoid margin calls, and make informed decisions before placing trades.
Key highlights:
- Inputs Needed: Account size, risk tolerance, stop-loss distance, tick size/value, and margin requirements.
- Core Outputs: Margin requirements, leverage ratio, position sizing, and risk/reward analysis.
- Importance: Prevents over-leveraging, ensures proper risk management, and helps avoid liquidation during volatile markets.
- Hardware Matters: High-performance systems, like those from DayTradingComputers, ensure real-time calculations without delays, especially during market stress.
Accurate calculations and reliable hardware are essential for successful futures trading. This combination helps traders stay prepared, even in fast-moving markets.
Futures Calculator How to Use
sbb-itb-24dd98f
Key Inputs and Core Calculations
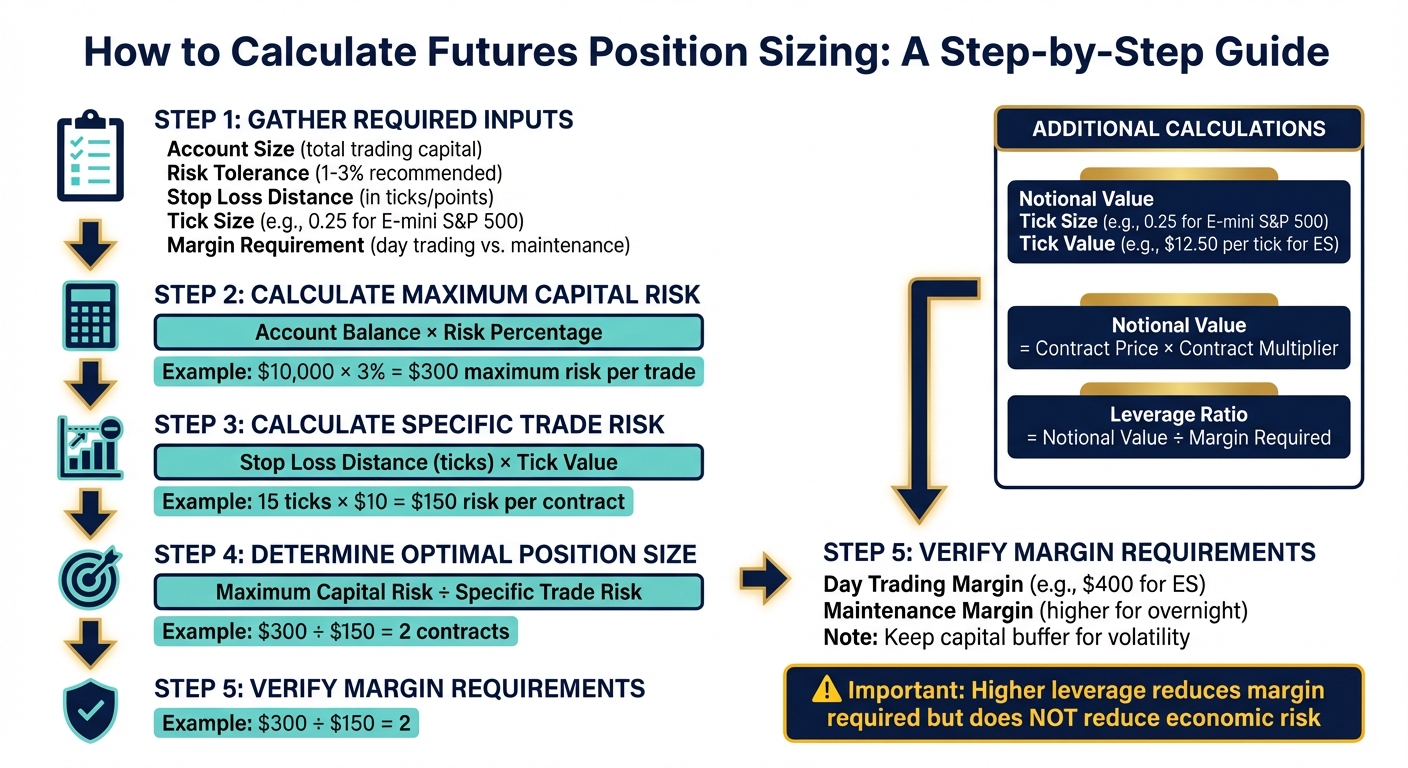
Futures Leverage Calculator: Step-by-Step Position Sizing Guide
Required Inputs for Calculations
To use a futures leverage calculator effectively, you’ll need six key inputs. First, there’s account size, which refers to the total amount of capital you’ve set aside for trading. Then comes risk tolerance, or the percentage of your account you’re comfortable risking on a single trade. Professional traders often stick to a range of 1% to 3% for this value. Another critical input is the stop loss distance, which measures how far the market can move against your position before you exit, typically expressed in ticks or points.
You’ll also need contract-specific details. The tick size defines the smallest price movement a contract can make (e.g., 0.25 for the E-mini S&P 500). The tick value translates that movement into dollar terms (e.g., $12.50 per tick for ES). Finally, the margin requirement specifies the minimum funds needed to open and maintain your position. This varies between day trading and overnight maintenance levels. These inputs are the backbone of accurate trade sizing.
Standard Calculation Formulas
Position sizing relies on three core formulas. Start by calculating your maximum capital risk, which equals your account balance multiplied by your risk percentage. For example, if you have a $10,000 account and risk 3%, your maximum risk per trade would be $300.
Next, determine your specific trade risk by multiplying the stop loss distance (in ticks) by the tick value. For instance, a 15-tick stop on WTI Crude Oil, with a $10 tick value, results in $150 of risk per contract. To find your optimal position size, divide the maximum capital risk by the specific trade risk: $300 ÷ $150 = 2 contracts.
Two additional calculations provide broader insights. The notional value (contract price × contract multiplier) represents your total market exposure. Meanwhile, the leverage ratio (notional value ÷ margin required) shows how much market exposure you’re controlling relative to your deposit. Keep in mind that while higher leverage reduces the margin required, it does not reduce the actual economic risk. Once you’ve calculated position sizing, it’s essential to align these figures with U.S. market margin specifications.
U.S. Futures Market Specifications
To comply with U.S. market regulations, it’s crucial to adjust your calculations based on specific margin requirements. U.S. futures trading involves two types of margins. The maintenance margin, set by exchanges like CME, is the minimum balance needed to hold positions overnight. On the other hand, day trading margin, set by brokers, applies only to intraday trades. For example, many brokers require just $400.00 for trading ES during the day.
Retail traders should also be aware of additional rules. The CFTC and NFA enforce a 10% higher margin requirement for retail traders compared to CME’s published rates. Another key rule is the 15-minute cutoff: day trading margins expire 15 minutes before the market closes. Traders must either exit their positions or meet full maintenance margins five minutes before the daily close. A notable example of how these rules come into play was the "Red Monday" event on September 22, 2025, when margin-call checks surged by 30–40% as traders scrambled to ensure their positions met the requirements.
How to Use a Futures Leverage Calculator
Entering Data and Calculating Margin
Once you understand the key inputs and formulas, using a futures leverage calculator becomes straightforward. Start by selecting your futures contract – whether it’s the E-mini S&P 500, Micro E-mini Nasdaq-100, or another option. Then, choose the trade direction (long or short) and input the following details: entry price, stop-loss, account balance, risk percentage, and your preferred leverage ratio.
If you don’t provide an entry price, the calculator will use the current market quote by default. Specify your stop-loss in ticks or points, following the format used by the market you’re trading. Add your account balance and the percentage of it you’re willing to risk per trade. Many experienced traders stick to a risk range of 1% to 3% per trade. Finally, enter the leverage ratio you plan to use. The calculator will then determine the margin requirement, which is the amount of capital that will be tied up to maintain your position.
Understanding the Results
The calculator provides several key outputs: margin requirement, position sizing, leverage ratio, tick value, and risk/reward ratio. It also distinguishes between day trading margin and maintenance margin, giving you a complete picture.
- Position sizing: Tells you how many contracts you can trade while staying within your risk limits.
- Leverage ratio: Shows your market exposure. For example, with a $1,000 account and 10× leverage, you control $10,000 in exposure.
- Tick value: Indicates the dollar amount of the smallest price movement, helping you set precise stop-loss levels.
- Risk/reward ratio: Confirms whether the potential reward justifies the risk, ensuring your trade decisions are calculated and deliberate.
"Increasing the leverage ratio reduces the margin required for entry, but it does not reduce the actual economic risk of the trade." – Leverage.Trading
Running Calculators on DayTradingComputers Hardware
Using reliable hardware can make a big difference in how smoothly these calculations run. Professional traders often juggle multiple tools at once, and DayTradingComputers hardware is designed to handle this type of multitasking. For example, you can keep the leverage calculator open on a secondary monitor while running your trading platform on the main screen. This setup is especially helpful for quickly recalculating position sizes if your entry price changes or market conditions become more volatile.
During times of high market activity, traders frequently check their margin buffers to avoid surprises. High-performance systems reduce delays, which is crucial when every second counts. With DayTradingComputers’ multi-monitor setups – supporting up to two screens even on entry-level systems – you can monitor everything from margin requirements to live charts and order execution without constantly switching windows. This streamlined workflow helps you stay focused and ready to act.
Risk Management with Leverage Calculators
Using Calculators in Your Risk Management Plan
Leverage calculators are a vital part of any risk management strategy. They provide a clear picture of your required margin and potential exposure before you even place a trade. By using these tools, you can see how much capital will be tied up, pinpoint your liquidation threshold, and determine the percentage of your account at risk. Many professional traders adhere to a strict rule of risking only 1% to 2% per trade, and calculators make it straightforward to stay within these boundaries.
For instance, after the market crash on September 22, 2025, simulations of futures trade setups surged by about 46% within 24 hours. This shift reflected traders moving from focusing on entries to prioritizing risk calibration. This highlights how calculators can discourage over-leveraging by clearly showing the risks of high leverage before you commit your funds.
"Risk management in leveraged markets starts with knowing exactly how much margin each position consumes. A calculator helps you see that number before you commit capital." – Leverage.Trading
Margin Requirements and Free Capital
A solid understanding of initial margin and maintenance margin is essential for managing leveraged trades. The initial margin, sometimes referred to as the day trading margin, is the minimum amount required to open a position during the trading session. On the other hand, the maintenance margin is the higher amount needed to keep that position open overnight.
If your account equity dips below the maintenance margin, you’ll face a margin call – a demand to either deposit more funds or close some positions. During periods of market volatility, margin requirements can jump unexpectedly. This is why keeping a capital buffer beyond the minimum margin is so important. That extra cushion helps you ride out market fluctuations without triggering forced liquidations. Leverage calculators can show you exactly how much free capital remains after opening a position, helping you prepare for sudden market swings.
Hardware Reliability for Risk Management
The accuracy of leverage calculators depends on the hardware that powers them, especially during volatile markets when every second matters. For example, U.S. traders ran approximately 2× more liquidation checks per user during high-stress trading events compared to calmer periods. If your trading platform freezes or lags at a critical moment, you could miss the chance to recalculate position sizes or confirm your margin buffer, leaving you vulnerable to forced liquidations.
DayTradingComputers offers hardware designed for high-performance trading, featuring multi-monitor setups and ample RAM to handle real-time recalculations. With a leverage calculator open on one screen and live charts or order execution on another, you can react quickly to shifting margin requirements or verify liquidation thresholds as market conditions change. Reliable hardware ensures you’re not caught off guard when it matters most.
Recommended Futures Margin and Leverage Tools
Top Futures Calculation Tools
If you’re navigating the fast-paced world of futures trading, having the right tools to calculate leverage, margins, and potential outcomes is a game-changer. Here are some of the best options available:
- Leverage.Trading: This web-based platform helps you calculate leverage ratios, margin requirements, and profit/loss. It also incorporates a "Risk-First" framework, which evaluates liquidation thresholds and funding costs.
- StoneX Futures Calculator: With this tool, you can select specific futures contracts – like the E-mini S&P 500 or Crude Oil – and calculate potential profit or loss in both ticks and USD. It’s tailored for market-specific scenarios.
- AMP Futures Margin Tool: This tool provides a detailed overview of maintenance and day trading margins across major exchanges, including CME, Eurex, and ICE. It’s particularly useful for understanding the capital needed for intraday and overnight positions.
- Insider-Week Futures Calculator: Ideal for position sizing, this calculator determines the number of contracts to trade based on a percentage of your account, ranging from 0.5% to 10%.
- CME Group Margin Calculators: As the official margin tools for Futures & Options and Interest Rate Swaps, these calculators offer authoritative data to help traders optimize their margin requirements.
- PropFirmPlus Margin Calculator: Designed for traders operating in multiple markets, this tool delivers instant margin calculations for Forex, CFDs, and Futures, helping to manage exposure effectively.
"As a futures trader, it is critical to understand exactly what your potential risk and reward will be in monetary terms on any given trade." – StoneX
These tools are invaluable for making informed trading decisions, especially when combined with reliable hardware.
How DayTradingComputers Improves Tool Performance
To make the most of these calculation tools, you need hardware that can keep up with the demands of real-time trading. High-stress market conditions call for systems that can handle multiple simulations and recalculations without delays.
DayTradingComputers offers trading computer setups specifically designed for traders, featuring high-capacity RAM and multi-monitor setups. For example, their Pro and Ultra models come equipped with 64GB and 128GB of RAM, ensuring smooth performance even when running several calculation tools alongside your trading platform. Multi-monitor configurations allow you to dedicate one screen to calculators while using others for live charts and order execution.
This hardware reliability is especially crucial during volatile market sessions. Imagine margin requirements skyrocketing by 200% – you need a system that can instantly recalculate position sizes without freezing. With DayTradingComputers, you can quickly reassess your risk exposure and seize opportunities without missing a beat. Their systems are built to handle the pressure, helping you stay ahead in dynamic trading environments.
Conclusion
Futures leverage calculators play a critical role in navigating volatile markets. By turning risk assumptions into clear, actionable numbers, these tools help traders determine liquidation thresholds, margin buffers, and optimal position sizes before placing trades. For instance, during the market crash in September 2025, traders who used pre-trade verification managed to protect their capital through defensive positioning. These calculators don’t just measure risk – they lay the groundwork for disciplined, data-driven trading.
"Your first profitable trade isn’t the one that makes money – it’s the one that doesn’t lose money." – Trading In Depth
Sticking to the 1–3% risk rule is another cornerstone of smart trading. Following the September crash, trade simulations jumped by 46%, highlighting how vital pre-trade verification is. Leverage calculators reinforce this discipline, showing exactly how many contracts fit safely within your risk tolerance.
But accurate calculations alone aren’t enough. Reliable hardware is equally important when executing these strategies. Professional traders depend on systems that perform consistently, even during extreme market swings. For instance, DayTradingComputers’ Pro and Ultra models, equipped with 64GB and 128GB of RAM respectively, ensure calculations run instantly across multiple tools and platforms. In a world where seconds can mean the difference between seizing an opportunity or hitting a margin call, hardware lag simply isn’t an option.
The key to successful futures trading lies in blending precise risk management with dependable technology. When you combine accurate data with reliable systems, you’re better equipped to make quick, informed decisions – even in the most turbulent markets.
FAQs
How can a futures leverage calculator help traders avoid over-leveraging?
A futures leverage calculator is a handy tool for traders looking to manage risk effectively. It quickly calculates the required margin and leverage ratio for a given trade, giving traders a clear picture of their potential exposure. This clarity helps them adjust their position sizes to stay within safer risk levels.
By delivering precise and instant insights, these calculators enable traders to make smarter decisions and avoid the dangers of over-leveraging, which can result in substantial losses.
What’s the difference between day trading margin and maintenance margin?
Day trading margin is the minimum amount of money a trader needs in their account to open and close positions within the same trading day. It gives traders the ability to use leverage more aggressively since they don’t hold positions overnight.
On the flip side, maintenance margin refers to the minimum equity that must remain in a trading account to keep a position open. If the account balance dips below this threshold, the broker may issue a margin call, requiring the trader to add funds to avoid having their position liquidated.
Grasping these concepts is key to managing risk effectively and staying compliant with trading rules.
Why is reliable computer hardware essential for using a futures leverage calculator?
Reliable computer hardware plays a key role in using a futures leverage calculator effectively. These calculators often demand quick and precise data processing, and a high-performance computer ensures calculations are done swiftly and without errors – critical when you’re making time-sensitive trading decisions.
On top of that, dependable hardware reduces the chances of system crashes or slowdowns, which could interrupt your workflow or even result in costly errors. By investing in solid, reliable equipment, traders can work more efficiently and accurately, giving them an edge in managing risks and making informed decisions.